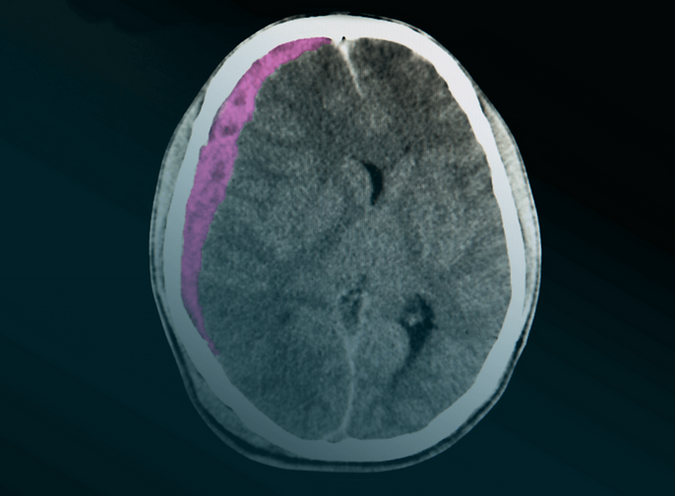
Subdural Hematomas & Head Injuries in Florida Nursing Homes, Assisted Living Facilities, Group Homes, & Adult Day Care Centers
What is a Subdural Hematoma?
A subdural hematoma, sometimes referred to as a brain bleed, is a collection of blood that forms on the surface of the brain, typically as a result of a trauma. This bleeding may press against brain tissue, causing swelling, impaired function, and potentially death. The most common causes in nursing homes, assisted living facilities, group homes, and adult day care centers are falls, head trauma, or resident-on-resident violence. Even seemingly minor head injuries can result in delayed-onset hematomas, especially in elderly or anticoagulated individuals.
Subdural hematomas are estimated to occur in roughly 25% of all head injuries. Among elderly residents, the risk may be even higher due to brain atrophy, frailty, and delayed response from facility staff.
Brain Bleeds Can Be Life-Threatening
A subdural hematoma can be life-threatening as a buildup of blood can cause pressure on the brain, leading to breathing problems, confusion, seizures, paralysis, strokes, and/or death. As such, it is critical for facilities, among other things, to screen residents for their fall risks, design an adequate and appropriate fall care plan, implement designated fall precautions, and revisit the care plan regularly and upon a change in the resident’s condition. It is also important for nursing homes, assisted living facilities, group homes, and adult day care centers to screen and monitor for violent residents to ensure they are neither a danger to themselves nor others.
What Often Gets Missed After a Head Injury
When a resident suffers a head injury, whether from a fall, being dropped, or striking a surface, delays in evaluation and treatment can lead to severe complications. In many cases, facilities fail to document the incident accurately, notify the physician, or conduct ongoing monitoring to identify changes in neurological status. Families are sometimes left in the dark, and injuries that could have been managed early become life-threatening due to missed symptoms or poor communication.
Contact FIDJ for a Free Case Review
If you believe your loved one sustained a head injury at a nursing home, assisted living facility, group home, or adult day care center, contact the experienced attorneys at FIDJ and obtain a FREE case review.
*The information contained herein is not medical advice.

They failed. Now, it's time to
Demand
Check out our latest blogs...

We Proudly Represent Clients In and Around These Major Florida Cities
Miami, Fort Lauderdale, West Palm Beach, Orlando, Tampa, Jacksonville, Sarasota, Naples, Fort Myers, Boca Raton, Hollywood, Lakeland, Ocala, Pensacola, Gainesville, St. Petersburg, Clearwater, Port St. Lucie, Melbourne, Tallahassee, Kissimmee, Cape Coral, Coral Springs, Vero Beach, St. Augustine, Port Charlotte, Panama City
...and these Florida regions
South Florida, Central Florida, North Florida, the Gulf Coast, Treasure Coast, Space Coast, the Panhandle, the Keys, Suncoast, Nature Coast, Big Bend, Emerald Coast, and First Coast.
What that Means
If you are searching for a "nursing home abuse lawyer near me", an "assisted living facility abuse lawyer near me", a "group home abuse lawyer near me", or an "adult day care center abuse lawyer near me", FIDJ has you covered.

Do you need an attorney who handles cases near you or your loved one? Our attorneys handle cases involving nursing home abuse and neglect, assisted living facility abuse and neglect, group home abuse and neglect, and adult day care center abuse and neglect in the following Florida counties: Alachua, Baker, Bay, Bradford, Brevard, Broward, Calhoun, Charlotte, Citrus, Clay, Collier, Columbia, DeSoto, Dixie, Duval, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Glades, Gulf, Hamilton, Hardee, Hendry, Hernando, Highlands, Hillsborough, Holmes, Indian River, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Lake, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Manatee, Marion, Martin, Miami-Dade, Monroe, Nassau, Okaloosa, Okeechobee, Orange, Osceola, Palm Beach, Pasco, Pinellas, Polk, Putnam, Santa Rosa, Sarasota, Seminole, St. Johns, St. Lucie, Sumter, Suwannee, Taylor, Union, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton, Washington.







